Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Our work in Coronavirus (COVID-19)
-
More Employers Should Mandate COVID-19 Vaccines for Workers — for the Health of their Business
If employers will want to operate reliable in-person workplaces and attract customers, they will have to embrace a solution that the government has so far shied away from: vaccine mandates.
Categorized in -
COVID-19 Vaccination Mandates for Employees and Students are Effective Tool Against Virus Spread
A new white paper finds private sector influence combined with market-side demand for mandates will overcome state laws that have limited vaccine requirements thus far.
Categorized in -
Racial and Ethnic Disparities in SARS-CoV-2 Testing and COVID-19 Outcomes in a Medicaid Managed Care Cohort
Though the study of racially diverse Medicaid patients indicated disproportionate risk among Latinos, USC researchers say it can’t be explained by higher rates of poverty or underlying health factors like obesity.
Categorized in -
Latinos Are More Likely to Die From COVID-19, Underlining Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Outcomes
Latinos were tested more for COVID-19 and had higher rates of infection, hospitalization and death.
Categorized in -
Mandatory Masking of School Children is a Bad Idea
The benefits of masks in preventing serious illness or death from COVID-19 among children are small. Meanwhile, they are disruptive to learning and communicating in classrooms.
Categorized in -
COVID-19 Vaccination Mandates for School and Work Are Sound Public Policy
A new Schaeffer Center white paper finds that vaccine mandates for employees and students is an effective policy solution to ensure the U.S. reaches herd immunity and avoids future outbreaks.
Categorized in -
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Policy Responses on Excess Mortality
To understand the net effects of shelter-in-place (SIP) policies, the researchers measure the change in excess deaths following the implementation of SIP policies in 43 countries and all U.S. states.
Categorized in -
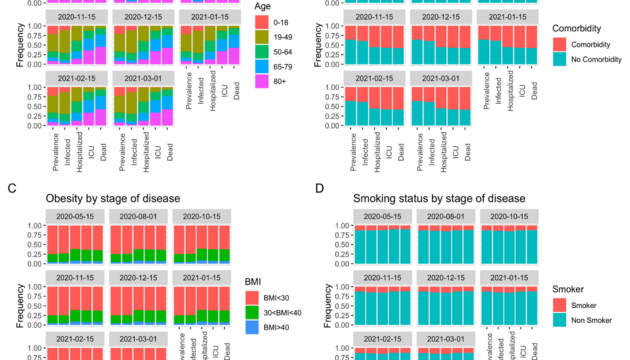
An Integrated Risk and Epidemiological Model to Estimate Risk-Stratified COVID-19 Outcomes for Los Angeles County: March 1, 2020—March 1, 2021
The researchers focus their modeling framework on the risk factors age, comorbidities, obesity, and smoking status as these demographic and medical conditions have consistently been identified across various studies as factors inducing the probability of progressing to severe illness given COVID-19 infection
Categorized in -
Reporting of Infectious Diseases in the United States During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic
Reporting of infectious diseases other than COVID-19 has been greatly decreased throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
Categorized in -
A Megastudy of Text-Based Nudges Encouraging Patients to Get Vaccinated at an Upcoming Doctor’s Appointment
This study evaluated the impact of 19 nudges delivered to patients via text message and designed to boost the adoption of the influenza vaccine.
Categorized in